Introduction
In vitro fertilization (IVF) represents a beacon of hope for many people and partners grappling with infertility. Around their explanation of many years, advancements in reproductive know-how have not only improved the odds of conception but also opened the doorway to a revolutionary treatment: preimplantation genetic prognosis (PGD). PGD will allow for the genetic screening of embryos prior to they are implanted in the uterus, making sure that only embryos without having determined genetic problems or abnormalities are selected for pregnancy. As we navigate through the twenty first century, PGD stands at the forefront of reproductive medicine, heralding a new era of genetic screening that claims to reshape the long run of IVF.
The Evolution of IVF and Genetic Screening
IVF has undergone a radical transformation because the birth of Louise Brown, the world’s to start with „check-tube newborn,“ in 1978. Early IVF methods were being marred by minimal achievements rates and restricted comprehending of embryonic development. The introduction of genetic screening was a game-changer, enabling embryologists to take a look at the genetic make-up of embryos and choose all those with the greatest prospective for a nutritious being pregnant.
The Growth of Preimplantation Genetic Analysis
PGD is a specialised strategy that includes getting rid of one particular or far more cells from an IVF embryo to check for certain genetic ailments right before the embryo is transferred to the uterus. Originally made to screen for intercourse-connected conditions, PGD has expanded to involve a vast assortment of genetic and chromosomal abnormalities.
Being familiar with the Genetic Screening Method
The procedure of PGD commences with the typical IVF cycle, the place eggs are harvested and fertilized in the lab. As soon as the embryos reach the blastocyst phase, a couple of cells are biopsied and analyzed applying a single of numerous genetic screening methods, such as polymerase chain response (PCR) or future-era sequencing (NGS). These approaches permit for the detection of single-gene disorders, chromosomal abnormalities, and even the potential for inherited most cancers syndromes.
The Ethics of Genetic Screening
As with several advances in biotechnology, PGD brings with it a host of ethical considerations. The potential to choose embryos centered on genetic standards has sparked discussion around the thought of „designer babies“ and lifted fears about eugenics. Ethicists and health-related professionals continue to grapple with these difficulties, striving to discover a balance in between the benefits of genetic screening and the ethical implications of genetic collection.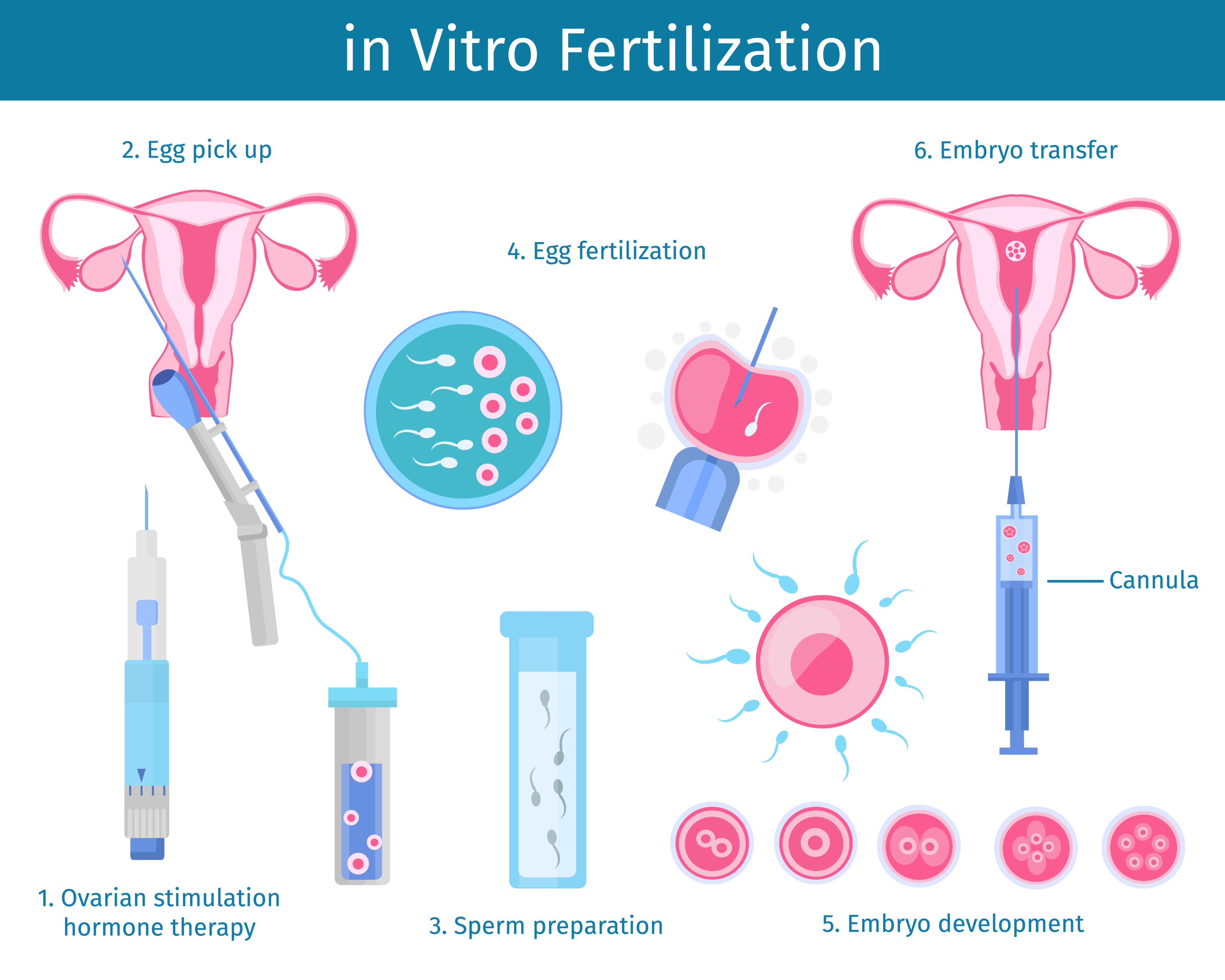
The Influence of PGD on Genetic Problems
PGD has experienced a profound affect on the avoidance of genetic conditions. Family members with histories of heritable problems like cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs ailment, or Huntington’s illness now have the selection to bear children without the concern of passing these situations on. This has not only diminished the incidence of specific genetic ailments but also alleviated the psychological and fiscal stress on people and healthcare methods.
Enhancements and Innovations in PGD
The field of PGD is consistently evolving, with new systems maximizing its precision and scope. The advent of detailed chromosomal screening (CCS) allows for the investigation of all 23 pairs of chromosomes, ensuring that only embryos with the proper number of chromosomes are implanted. This has drastically decreased the threat of miscarriages and improved the good results rates of IVF.
The Job of PGD in Loved ones Balancing and Gender Assortment
A person of the much more controversial areas of PGD is its use in family balancing and gender assortment. Some argue that the capacity to pick the sexual intercourse of one’s baby is a all-natural extension of reproductive freedom, even though other individuals fear about the social and demographic outcomes of this sort of selections. However, in circumstances wherever gender-particular genetic disorders are a worry, gender range continues to be a essential element of PGD.
The Potential of PGD: Increasing the Alternatives
As we glance to the future, PGD is poised to broaden in abilities. Analysis into polygenic chance scores could empower PGD to display screen for complicated disorders like heart sickness or diabetic issues, which are influenced by various genes. There is also the opportunity to use PGD in conjunction with gene editing technologies like CRISPR, to not only choose but also suitable embryos at the genetic level, though this continues to be ethically and lawfully contentious.
Legal and Regulatory Concerns
The regulation of PGD differs substantially all-around the environment, with some nations embracing the technology and other people imposing rigorous restrictions. As the science progresses, policymakers will be challenged to create frameworks that make certain ethical apps of PGD while supporting scientific progression.
Conclusion
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis stands at the intersection of genetics, medicine, and ethics, presenting unparalleled manage in excess of the genetic health and fitness of foreseeable future generations. Its integration with IVF has previously improved the potential customers of would-be mother and father to have healthy young children and claims to keep on its trajectory of innovation in the realm of reproductive health and fitness. As we progress, it is vital that we take into consideration the ethical implications and lawful frameworks important to information the accountable use of this strong know-how. The potential of PGD in IVF is not just about the science of genetics, but also about the values we as a modern society opt for to uphold